Introduction
htop is an interactive process viewer. It is a cross-platform tool used to monitor system processes in real-time.
Similar to the top command, htop provides an improved user interface with additional features.
It allows users to scroll vertically and horizontally through the list of running processes, providing detailed information such as memory and CPU consumption. Also system wide information, like load average or swap usage, is shown.
This article will delve into the utility of the htop command in Linux, helping you understand its syntax, options, and practical use-cases.
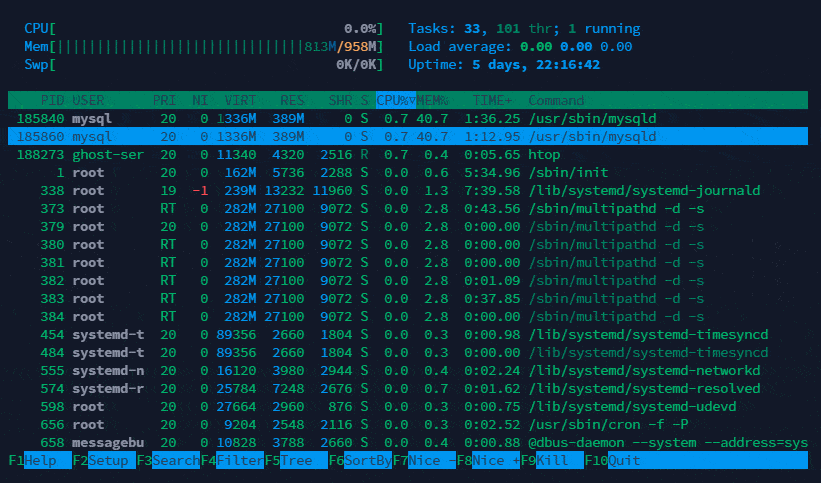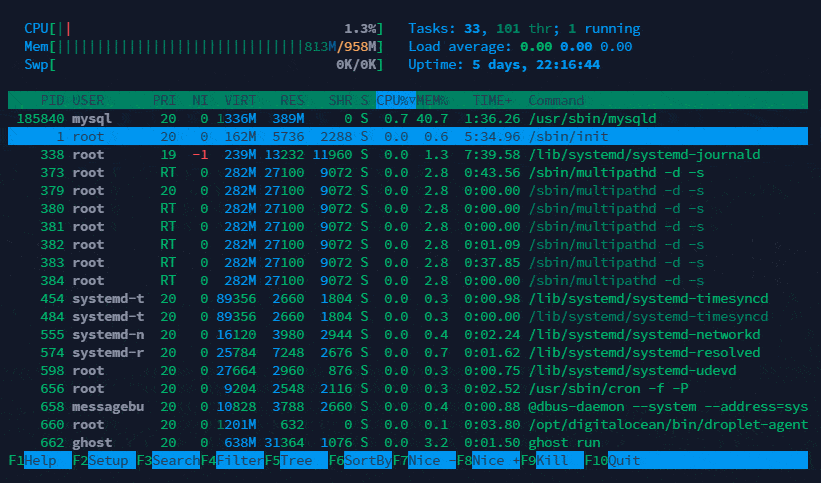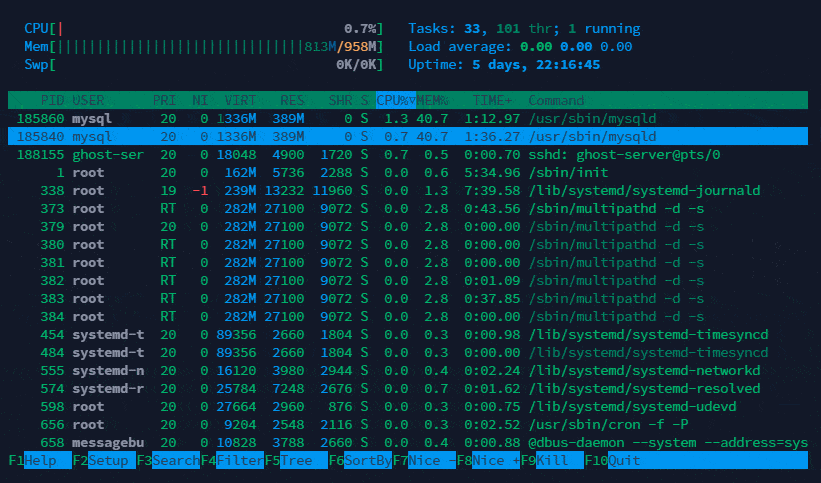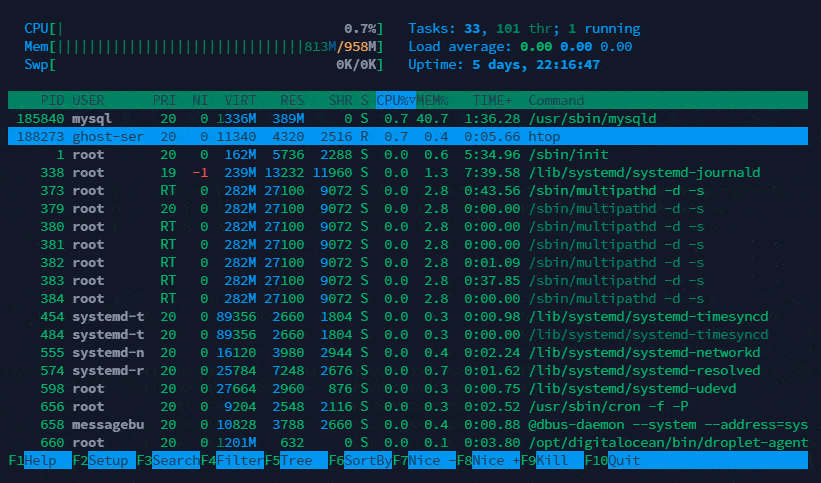
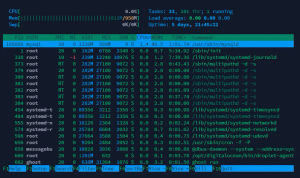
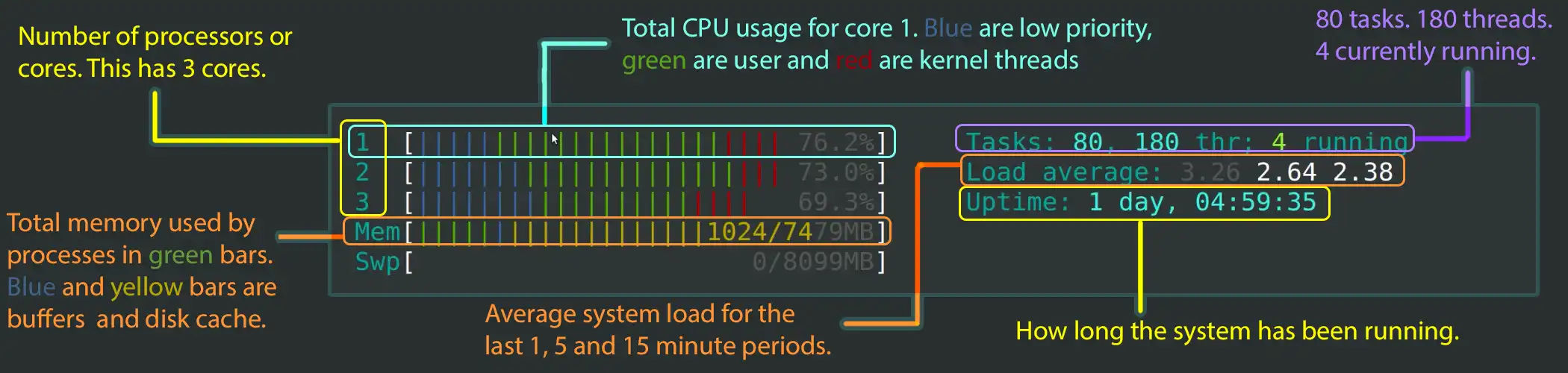
Below is upper section explanation which shows overall usage value of CPU, Memory and tasks.
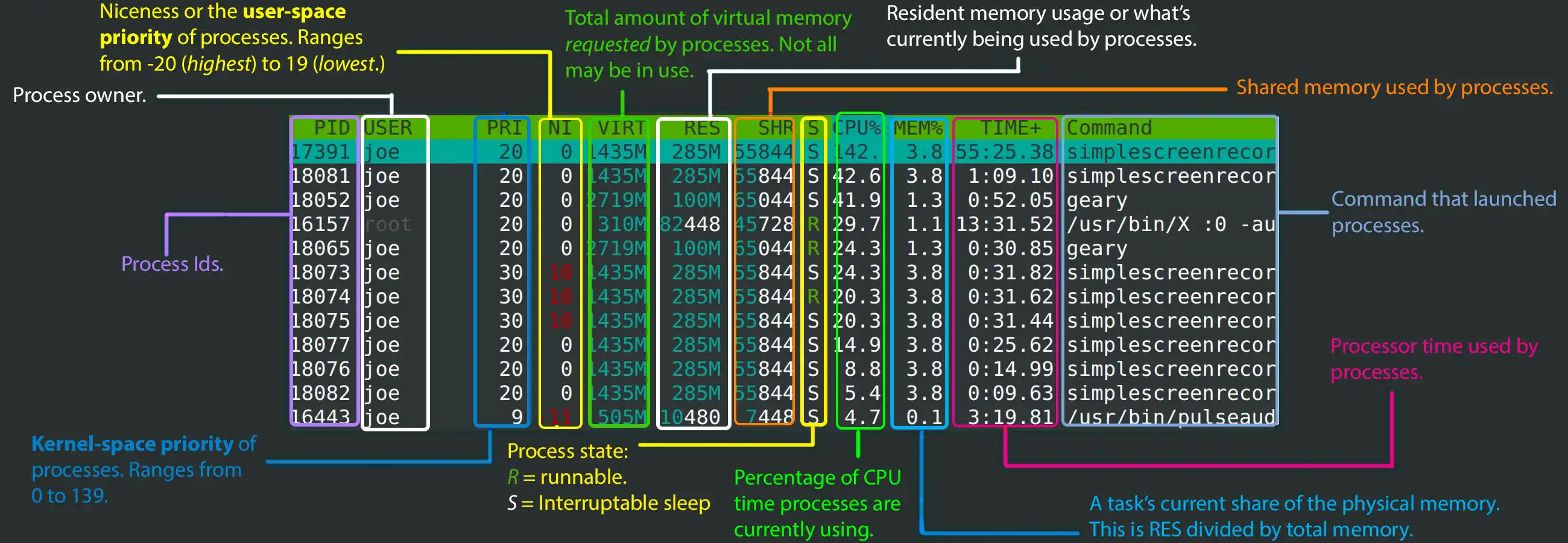
Below is lower section explanation which shows process wise usage value of CPU, Memory and tasks.
htop Command Options
- Displays updated process information every second.
htop -d 10- htop displays the output without any color.
htop -C- Displays only the processes running under the user 'root'.
htop -u rootAdvance Usage in htop interface
- Filter Processes by Name: Press F4 then enter the process name.
- Tree View : Press F5.
- To kill a process : Navigate using arrow keys, then press F9 and select a signal to send (use
sudo htopif killing root process).
Binaries
Packages for htop are available in most distros. Try the package manager from your system, chances are htop is available from there.
- GoboLinux: In GoboLinux you can fetch and compile htop by typing:
Compile htop - Debian: You can download the binary packages from the Debian webpage. or you can fetch htop by typing:
apt install htop - Fedora: htop is included in the Fedora repositories; you can fetch it with:
dnf install htop - RedHat: You can find RPM packages at EPEL.
- Slackware: htop is part of Slackware. You can find it in the ap/ section.
- Gentoo: In Gentoo Linux you can emerge the sys-process/htop package by typing:
emerge sys-process/htop - AltLinux: here are the latest RPMs for AltLinux.
- OpenSuSE: htop is included in the OpenSuSE build service.
- Arch Linux: htop is included in Arch Linux official repositories, you can get it with:
pacman -S htop